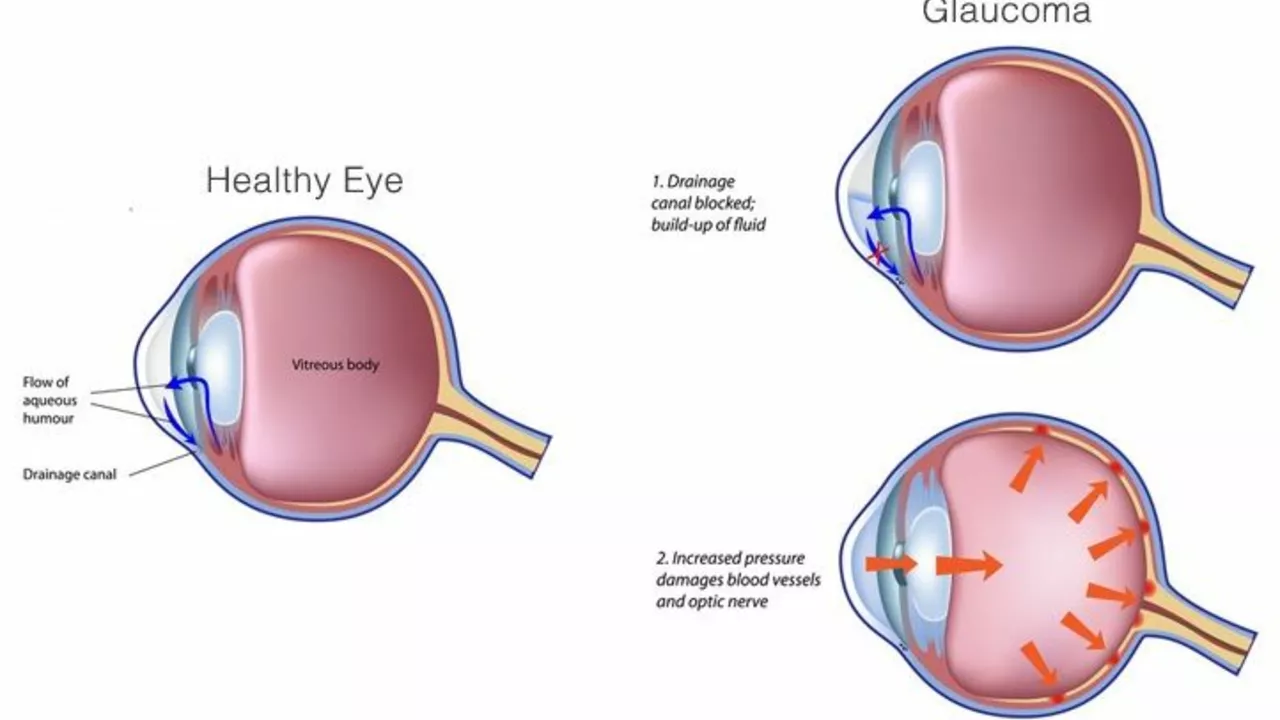
Understanding High Eye Pressure
High eye pressure, also known as ocular hypertension, refers to a condition where the pressure inside the eye, or intraocular pressure, is higher than normal. It is important to note that high eye pressure does not necessarily equate to glaucoma, but it is indeed a risk factor. The normal eye pressure ranges between 12-22 mm Hg, and anything beyond this can be considered high. This condition can be asymptomatic, which means it might not show any symptoms. It is usually detected during routine eye check-ups, making them incredibly essential.
Health Conditions That Can Lead to High Eye Pressure
Several health conditions can increase the risk of high eye pressure. Diabetes is one such condition. People with diabetes are more prone to eye-related issues, including glaucoma and high eye pressure. Hypertension or high blood pressure is another condition that can contribute to high eye pressure. Also, people with thyroid conditions, specifically hypothyroidism, can have an increased risk. Other conditions include heart diseases, eye injuries, and certain types of eye surgeries.
Age and Genetic Factors
Age is a significant risk factor for high eye pressure. As you age, the risk of developing this condition increases. People over the age of 40 have a higher risk, and this risk continues to increase with each decade of life. Genetics also play a major role. If you have a family history of high eye pressure or glaucoma, your chances of developing these conditions increase. It's crucial to be aware of your family's eye health history and to share this information with your eye doctor.
Impact of Lifestyle Choices on Eye Pressure
Lifestyle choices can significantly impact eye pressure. Smoking, for instance, can increase your risk of high eye pressure and other serious eye conditions. A diet high in sodium can also contribute to higher eye pressure. Lack of physical activity and excessive caffeine or alcohol consumption can lead to an increase in eye pressure as well. Therefore, making healthier lifestyle choices can help keep your eye pressure within the normal range.
Preventive Measures and Healthy Habits
While you cannot control factors such as age and genetics, there are measures you can take to reduce your risk of high eye pressure. Regular eye check-ups are crucial in detecting any abnormal increase in eye pressure at an early stage. Staying physically active and maintaining a balanced diet can also help. Quitting smoking and limiting your consumption of alcohol and caffeine can significantly reduce the risk. Moreover, staying well-hydrated and reducing your sodium intake can help maintain normal eye pressure.
Treatment Options for High Eye Pressure
While high eye pressure can be a risk factor for glaucoma, it does not always require treatment. If your eye doctor determines that your high eye pressure puts you at risk of developing glaucoma, they may recommend treatments to lower your eye pressure. These could include prescription eye drops, laser treatment, or surgery. It's important to have regular follow-ups with your eye doctor, as they will monitor your condition and adjust your treatment as needed.



Katherine M
July 21, 2023 AT 20:52High ocular pressure, though often silent, intertwines with systemic health in subtle ways.
When sodium intake climbs, the eye’s fluid dynamics may shift, nudging intra‑ocular pressure upward.
Maintaining regular ophthalmic exams provides a safeguard against unnoticed escalation.
💡 A balanced diet and consistent activity can serve as a gentle buffer.
Remember, genetics set the stage, but lifestyle writes the script.
Bernard Leach
July 29, 2023 AT 15:32Ocular hypertension is not merely a statistic in a textbook; it represents a dynamic equilibrium that can tip under many influences. The trabecular meshwork acts as a drainage canal, and when its function wanes, pressure builds. Age gradually diminishes the elasticity of ocular tissues, making them less resilient. Hypertension in the bloodstream mirrors the ocular vasculature, and spikes can reverberate within the eye. Diabetes introduces microvascular changes that compromise filtration. Salt, often overlooked, attracts fluid retention that may extend to the ocular compartment. Caffeine, though modest, can cause temporary spikes that accumulate with frequent consumption. Alcohol, especially in excess, alters hormonal balances that influence intra‑ocular pressure. Smoking introduces oxidative stress, reducing the eye’s protective mechanisms. Physical inactivity reduces overall circulatory efficiency, limiting the eye’s ability to regulate pressure. Genetic predisposition provides the baseline risk, but lifestyle choices sculpt the trajectory. Regular eye examinations act as early warning systems, catching subtle shifts before damage ensues. Eye drops, when prescribed, target the production or outflow of aqueous humor, offering pharmacologic control. Laser trabeculoplasty can reshape drainage pathways, lowering pressure without medication. In refractory cases, surgical interventions create new channels for fluid egress. Ultimately, a holistic approach-diet, exercise, cessation of harmful habits, and medical oversight-offers the best defense against progression.
Shelby Larson
August 6, 2023 AT 10:12Honestly the link between salty snacks and eye pressure is real, dont ignore it.
People think a little salt wont matter but it adds up fast.
Mark Eaton
August 14, 2023 AT 04:52Getting moving isn’t just good for your heart-your eyes thank you too!
Even a brisk 30‑minute walk can help regulate fluid balance.
Stay active and keep that pressure in check.
Alfred Benton
August 21, 2023 AT 23:32One must consider that pharmaceutical interests often downplay lifestyle factors to promote costly eye‑drop regimens.
While research acknowledges diet, the emphasis remains on medication.
Thus, a critical eye on the sources is advisable.
Susan Cobb
August 29, 2023 AT 18:12It is fascinating how mainstream health advice consistently oversimplifies the nuanced interplay between nutrition and ocular physiology.
The reductionist view neglects the subtle hormonal cascades triggered by excess sodium.
One might argue that true expertise lies in appreciating these complexities.
Nevertheless, public guidelines rarely reflect such depth.
Ivy Himnika
September 6, 2023 AT 12:52Regular ophthalmic assessments remain the cornerstone of early detection.
Adopting a Mediterranean‑style diet, rich in antioxidants, further supports ocular health.
😊 Consistency in these practices yields measurable benefits.
Nicole Tillman
September 14, 2023 AT 07:32While salty foods can influence fluid retention, individual susceptibility varies widely.
Sue Holten
September 22, 2023 AT 02:12Oh sure, just quit coffee and the universe will hand you perfect vision-no big deal!
But seriously, small tweaks add up more than you think.
Tammie Foote
September 29, 2023 AT 20:52Complexities aside, most readers just need clear actionable steps.
Jason Ring
October 7, 2023 AT 15:32i think the eye doc reccmmends yearly checks, n dont skip them.
Kelly Hale
October 15, 2023 AT 10:12The battlefield of our daily choices is waged upon the delicate canvas of our eyes.
Each smoked cigarette is a tiny incendiary, each salty bite a slow‑burning ember.
When we ignore these sparks, the inferno of high pressure looms.
Yet within our grasp lies the weapon of moderation, the shield of activity.
Embrace it, and the saga turns from tragedy to triumph.
Neviah Abrahams
October 23, 2023 AT 04:52yeah walking does help but most ppl just sit all day
Uju Okonkwo
October 30, 2023 AT 22:32Remember that community support can make lifestyle changes easier; sharing recipes and workout tips fosters accountability.
It’s okay to start small and build momentum over time.
Together we can keep our eyes healthy.
allen doroteo
November 7, 2023 AT 17:12Honestly, the hype around diet and eye pressure is overblown.
Corey Jost
November 15, 2023 AT 11:52It’s tempting to blame every health issue on a single factor, yet such reductionism oversimplifies reality.
High intra‑ocular pressure emerges from a mosaic of genetics, systemic health, and habits.
Focusing solely on sodium ignores the broader context of cardiovascular wellness.
Moreover, the evidence linking moderate caffeine to sustained pressure spikes remains inconclusive.
Thus, while dietary awareness is valuable, it should not eclipse comprehensive medical evaluation.
Balance, not panic, is the prudent path forward.
Nick Ward
November 23, 2023 AT 06:32Great overview! 👍
felix rochas
December 1, 2023 AT 01:12The mainstream narrative deliberately obscures the truth!; they push drops while ignoring simple fixes!; Wake up and demand transparency!.
inder kahlon
December 8, 2023 AT 19:52Consider reducing processed foods and monitoring caffeine intake; both steps have measurable impact.